Exact Inference
Context
- By default, BayesiaLab constructs a Junction Tree from the given Bayesian network to perform Exact Inference.
- BayesiaLab constructs a Junction Tree as you switch from Modeling Mode
F4to Validation ModeF5for a given Bayesian network model for the first time. - Constructing such a Junction Tree can be very time- and memory-consuming depending on the network size and complexity.
- However, once the Junction Tree is constructed, performing inference is very quick.
- Whenever you modify your network (structure or parameters), BayesiaLab needs to recreate the entire Junction Tree again.
Usage
- You can specify to use Exact Inference by selecting
Main Menu > Inference > Exact Inference.
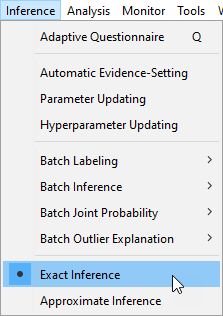
- By default, Exact Inference is active whenever you build or learn a new Bayesian network.
- In certain cases, the memory requirements or the expected computing time for creating the Junction Tree can be prohibitive.
- If you switch from Modeling Mode
F4to Validation ModeF5in such a situation, BayesiaLab may display a warning and offer you several options depending on the severity of the situation:
| Condition | Exact Inference will be very time-consuming | Exact Inference will not be possible |
|---|---|---|
| Options | 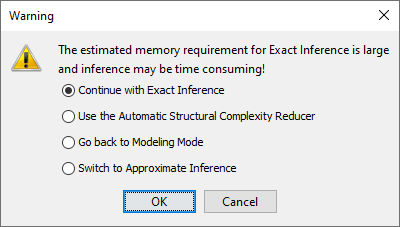 | 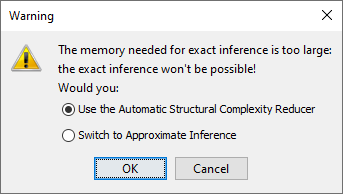 |
| Continue with Exact Inference | - You can still proceed with Exact Inference despite the warning. - However, you may face a long wait or encounter system stability issues. | n/a |
| Use the Automatic Structural Complexity Reducer | - You can take advantage of the Automatic Complexity Reducer, which removes less important arcs in the network. - To do so, the Automatic Complexity Reducer uses the dataset associated with the current network — or generates one according to the probability distributions — to compute the importance of each arc in the network. - The Automatic Complexity Reducer deletes the least important arcs until Exact Inference becomes possible in terms of memory and computation time. - The Automatic Complexity Reducer concludes its process by displaying a report listing all arcs that were deleted. | - You can take advantage of the Automatic Complexity Reducer, which removes less important arcs in the network. - To do so, the Automatic Complexity Reducer uses the dataset associated with the current network — or generates one according to the probability distributions — to compute the importance of each arc in the network. - The Automatic Complexity Reducer deletes the least important arcs until Exact Inference becomes possible in terms of memory and computation time. - The Automatic Complexity Reducer concludes its process by displaying a report listing all arcs that were deleted. |
| Go back to Modeling Mode | - You can return to the Modeling Mode F4 so you can modify the network yourself. | n/a |
| Switch to Approximate Inference | - Using Approximate Inference avoids the memory problem but sacrifices inference precision. Also, many types of analyses in BayesiaLab only work with Exact Inference. | - Using Approximate Inference avoids the memory problem but sacrifices inference precision. Also, many types of analyses in BayesiaLab only work with Exact Inference. |
Bear in mind that most of BayesiaLab’s analysis tools and functions require Exact Inference. They will not work with Approximate Inference.
