Overall Analysis — Node Force
Context
- The Node Force measure quantifies the importance of an individual node with regard to the entire Bayesian network structure of which it is a part.
- The Node Force can be especially relevant in networks without a Target Node, as the Node Force is not calculated vis-à-vis an individual node, but rather relative to the entire network.
- BayesiaLab computes three variants of the Node Force, which are all based on the Kullback-Leibler Divergence (Arc Force).
- The Entering Node Force is the sum of the Arc Forces of all arcs directed towards the node.
- The Exiting Node Force is the sum of the Arc Forces of all arcs directed away from the node.
- The Total Node Force is the sum of the Arc Forces of all arcs connected to the node.
Usage
- To activate the Node Force visualization, select
Main Menu > Analysis > Visual > Overall > Node Force.
Using the Control Panel
- Upon activation, the only thing that changes is the Toolbar. At the far end of the Toolbar, a control panel is added:

- There are three icons, roughly in the center of the control panel, which allow you to select the type of Node Force to use as a criterion for display:
- Entering Node Force:
- Total Node Force:
- Exiting Node Force:
- In the following screenshots and animation, we show the Total Node Force, but the process would be entirely the same for the other two measures.
- When starting the analysis, the controller shows 0 as the threshold for the Node Force values. This means that all nodes with a Node Force greater than 0 will be included initially.
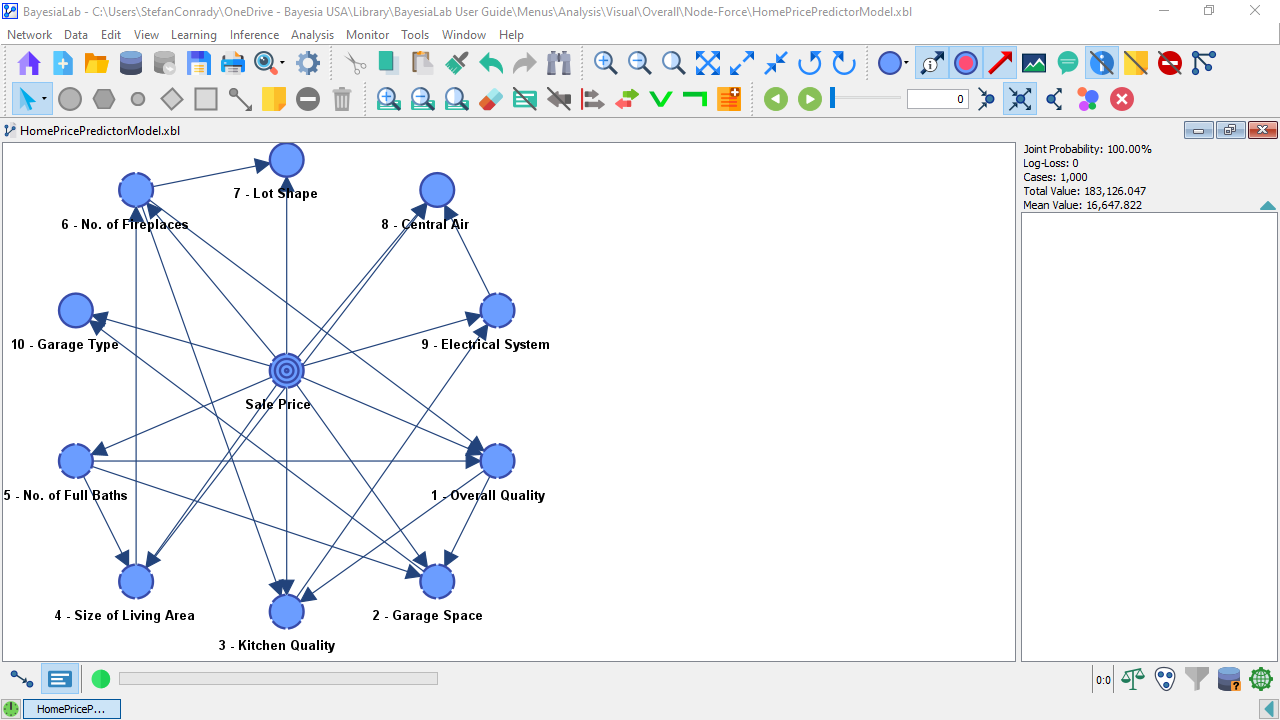
- In general, in a machine-learned network, all connected nodes are displayed as normal.
- You can modify the Node Force threshold in three ways:
- Using the previous/next buttons to skip to the next threshold level, which updates the display.
- By clicking next, the threshold jumps to the level of the node with the smallest Node Force.
- Clicking next again, that node “drops out.” More precisely, the node’s appearance changes to translucent, along with all arcs that connect to it.
- Alternatively, you can move the slider in the controller to scan a range of thresholds, which quickly gives you a sense of which nodes “drop out” at what level.
- Finally, you can also type a value into the controller field directly.
- Using the previous/next buttons to skip to the next threshold level, which updates the display.
- To end the analysis, click the stop icon .
Workflow Animation (1 of 2)
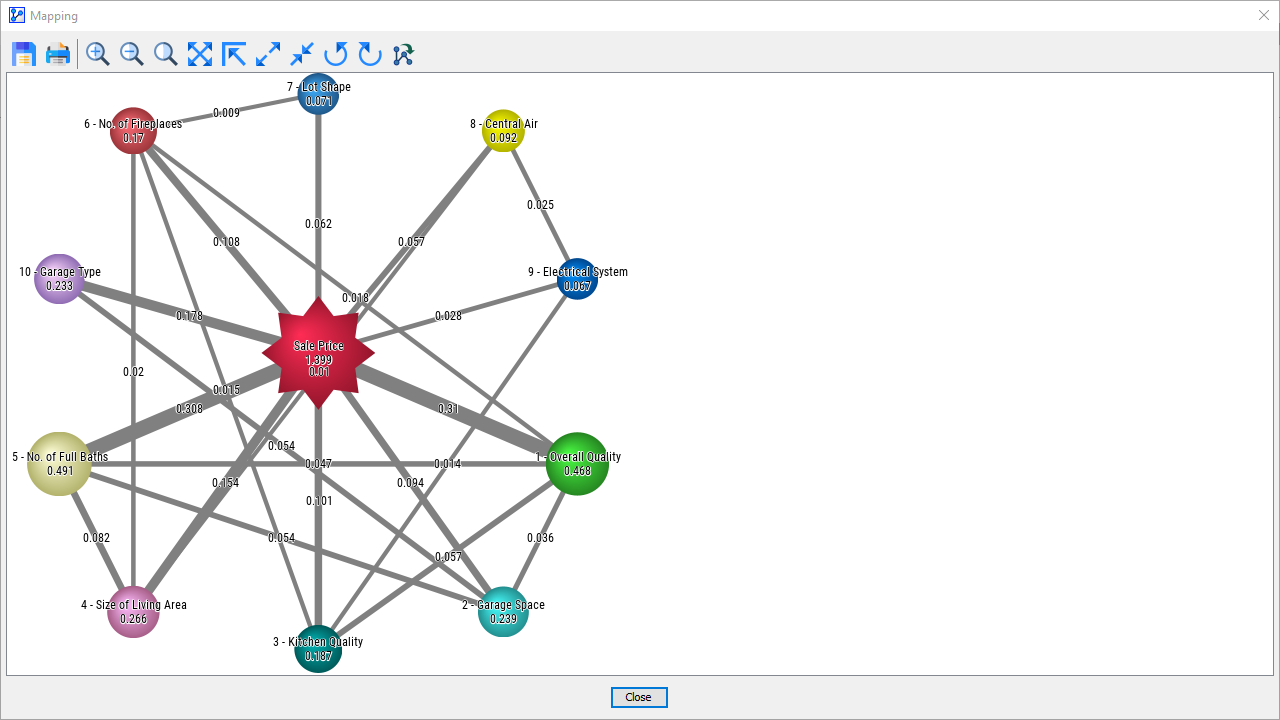
Mapping Function
-
The Mapping function significantly enhances the visual appeal and the interpretability of the Node Force display.
-
As opposed to merely toggling the display of nodes above and below a certain Node Force threshold, Mapping visualizes the Node Force.
-
While the Node Force analysis is active, you can open a new Mapping window by clicking the corresponding button in the control panel.
-
The network in the Mapping window mirrors the network structure in the Graph Panel but adds several important features:
- The nodes are now displayed as colorful spheres or “bubbles.”
- The size of each node is proportional to its Node Force, and the absolute value of the Node Force is displayed as a numerical value on the node.
- Additionally, the thickness of the arcs is proportional to the Kullback-Leibler Divergence (Arc Force). The value of the Arc Force is also attached as a label on the arcs.
- In this view, we can easily see how the Arc Forces add up to the Node Forces.
- The Target Node is highlighted with a star shape, although it is not treated differently here than any of the other nodes. Simply by virtue of its many connections, it happens to be the node with the strongest Node Force.
- The following screenshot displays the Total Node Force again, i.e., the same measure that we illustrated in the above animation.