Stratification
Context
- There are many research questions in which the cases of interest are very rare compared to regular observations.
- For example, when modeling fraud, the number of fraudulent transactions is presumably small compared to legitimate transactions.
- As a result, it would be difficult for a learning algorithm to detect associations between nodes related to those rare instances of fraud.
- With Stratification, you can modify the probability distributions within nodes by creating internal weights for specific states, i.e., the rare but important states.
- The probability distributions that are modified in this way push the learning algorithm towards discovering a network that is structurally more complex and can, thus, better represent rare observations.
- However, once the structure is learned, the parameters, i.e., the Conditional Probability Tables, are estimated on the original, unstratified dataset.
Usage
-
Select the nodes to be stratified.
-
Go to
Main Menu > Learning > Stratification. -
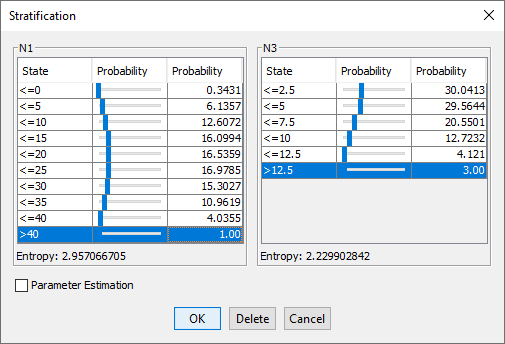
A dialog box opens in which you can specify the proportions of each state of the selected nodes.
-
The marginal distributions of the selected nodes are shown in separate panels.
-
At the bottom of each panel, the Entropy values that correspond to the distributions are shown.
-
Move the sliders to set the proportions to the desired levels or type the percentages directly:
-
As you change the probability, the Entropy values are updated.
-
Once you confirm the probabilities by clicking OK, the Stratification is set.
-
All stratified nodes are now marked with the Stratification indicator.
-
Additionally, the database icon in the Status Bar is tagged with a Stratification icon.
-
You can remove the Stratification by right-clicking on the icon in the Status Bar and then selecting Remove Stratification from the Context Menu.
