Symmetric Relative Mutual Information
Definition
Symmetric Relative Mutual Information computes the percentage of information gained by observing and :
This normalization is calculated similarly to Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient .
where denotes variance.
So, Mutual Information is comparable to covariance, and Entropy is analogous to variance.
Usage
For a given network, BayesiaLab can report the Symmetric Relative Mutual Information in several contexts:
- Select
Menu > Analysis > Report > Relationship Analysis:
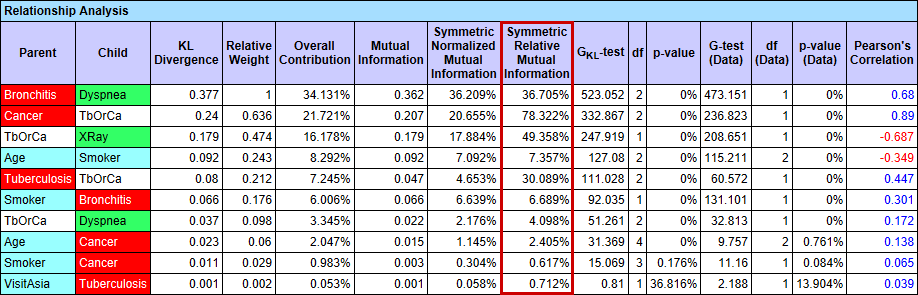
- The Symmetric Relative Mutual Information can also be shown by selecting
Menu > Analysis > Visual > Overall > Arc > Mutual Informationand then clicking the Show Arc Comments icon or selectingMenu > View > Show Arc Comments.
Loading SVG...
- Note that the corresponding options under
Preferences > Analysis > Visual Analysis > Arc's Mutual Information Analysishave to be selected first:
Loading SVG...
- In Preferences, “Child” refers to the Relative Mutual Information from the Parent onto the Child node, i.e., in the direction of the arc, always shown in blue.
- Conversely, “Parent” refers to the Relative Mutual Information from the Child onto the Parent node, i.e., in the opposite direction of the arc, always shown in red.
- Symmetric metrics are shown in black.
