Relative Mutual Information
Definition
Based on Mutual Information, Relative Mutual Information is defined as:
Relative Mutual Information expresses in percent how much the entropy (or uncertainty) of is reduced by observing .
- In older versions of BayesiaLab, Relative Mutual Information was also called Normalized Mutual Information.
- Please see the up-to-date definition of Normalized Mutual Information.
Usage
- BayesiaLab reports the Relative Mutual Information in the Target Analysis Report:
Menu > Analysis > Report > Target > Relationship with Target Node. - Note that this table shows the Relative Mutual Information of each node, e.g., XRay, Dyspnea, etc., only with regard to the Target Node, Cancer.
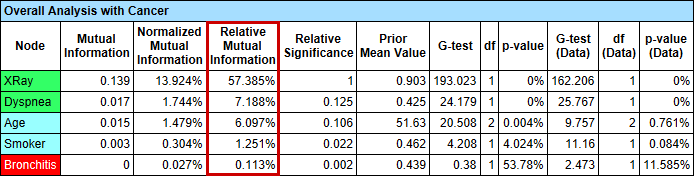
- The Relative Mutual Information can also be shown by selecting
Menu > Analysis > Visual > Overall > Arc > Mutual Informationand then clicking the Show Arc Comments icon or selectingMenu > View > Show Arc Comments.
Loading SVG...
- Note that the corresponding options under
Menu > Preferences > Analysis > Visual Analysis > Arc's Mutual Information Analysishave to be selected first:
Loading SVG...
- In Preferences, Child refers to the Relative Mutual Information from the Parent onto the Child node, i.e., in the direction of the arc.
- Conversely, Parent refers to the Relative Mutual Information from the Child onto the Parent node, i.e., in the opposite direction of the arc.
