Mutual Information
The Mutual Information measures the amount of information gained on variable (the reduction in the Expected Log-Loss) by observing variable :
The Venn Diagram below illustrates this concept:
Loading SVG...
The Conditional Entropy measures, in bits, the Expected Log-Loss associated with variable once we have information on variable :
Hence, the Conditional Entropy is a key element in defining the Mutual Information between and .
Note that
is equivalent to:
and furthermore equivalent to:
This allows computing the Mutual Information between any two variables.
Usage
For a given network, BayesiaLab can report the Mutual Information in several contexts:
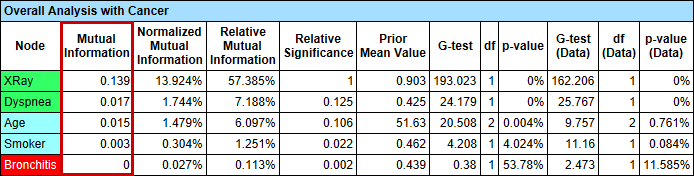
Main Menu > Analysis > Report > Target > Relationship with Target Node.- Note that this table shows the Mutual Information of each node, e.g., XRay, Dyspnea, etc., only with regard to the Target Node, Cancer.
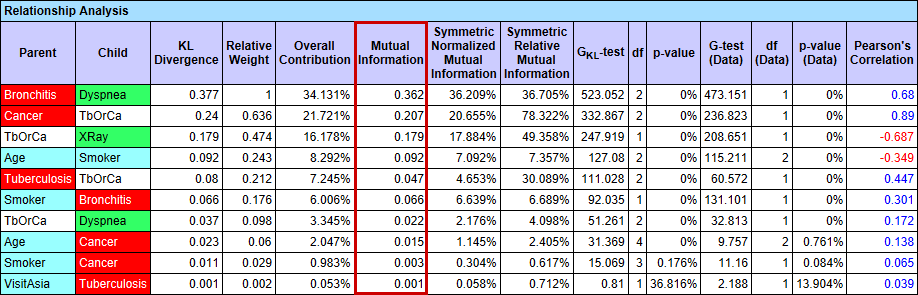
Main Menu > Analysis > Report > Relationship Analysis:
- The Mutual Information can also be shown by selecting
Main Menu > Analysis > Visual > Overall > Arc > Mutual Informationand then clicking the Show Arc Comments icon or selectingMenu > View > Show Arc Comments.
Loading SVG...
- Note that the corresponding options under
Preferences > Analysis > Visual Analysis > Arc's Mutual Information Analysishave to be selected first:
Loading SVG...
- In Preferences, Child refers to the Relative Mutual Information from the Parent onto the Child node, i.e., in the direction of the arc.
- Conversely, Parent refers to the Relative Mutual Information from the Child onto the Parent node, i.e., in the opposite direction of the arc.
