Impact on Target
Context
-
This feature compares a segment to a selected benchmark, either the entire dataset or another segment.
-
The comparison is done in terms of impacts, combining the difference between the observable variables’ mean values and their effect on the Target Node.
-
The Impact for each observable variable is computed as follows:
, where:
- is the analyzed segment,
- is the benchmark,
- is the mean value of in the data defined by the segment, is the mean value of in the data defined by the benchmark,
- is the effect of on the Target Node, evaluated on the benchmark.
-
Four types of effects can be calculated:
- Total Effect
- Standardized Total Effect
- Direct Effect
- Standardized Direct Effect
Example
- Let’s take the Perfume example for which we have defined five segments with the Breakout Variable Product, namely Prod3, Prod4, ProdG1, ProdG5, and ProdG6.
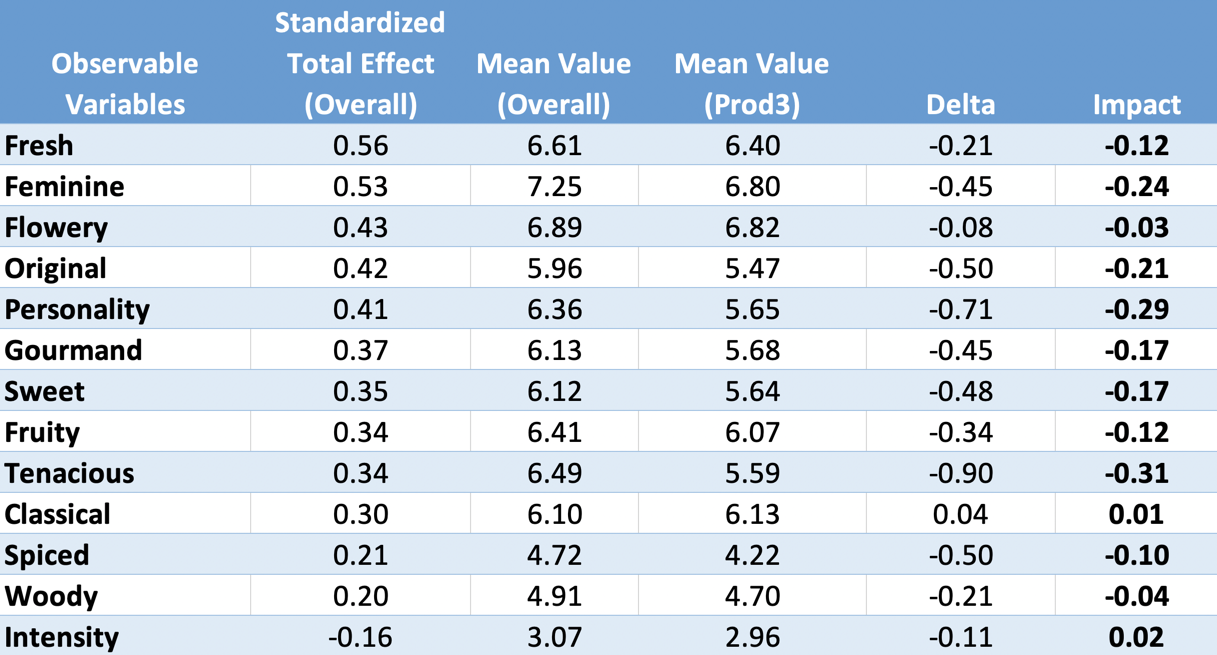
Below is the table with the Standardized Total Effects of all the observable variables on Purchase Intent and the mean values of these variables, computed on the entire dataset and on the segment represented by Prod3. These figures allow you to compute the Impacts of each variable.
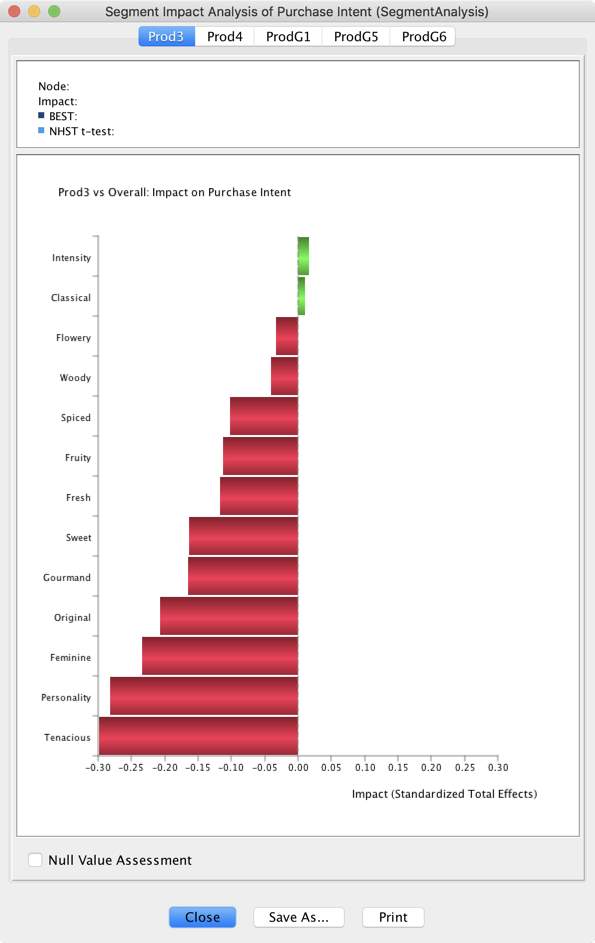
Null Value Assessment
-
This option allows estimating whether the segment and benchmark mean values are significantly different. Two tests are proposed for answering this question:
- A frequentist one: NHST t-test (Null Hypothesis Significance Testing) with Welch’s two-sample, two-tailed t-test.
- A Bayesian one: BEST, described in the paper by John K. Kruschke, “Bayesian Estimation Supersedes the t-test”, Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 2013.
-
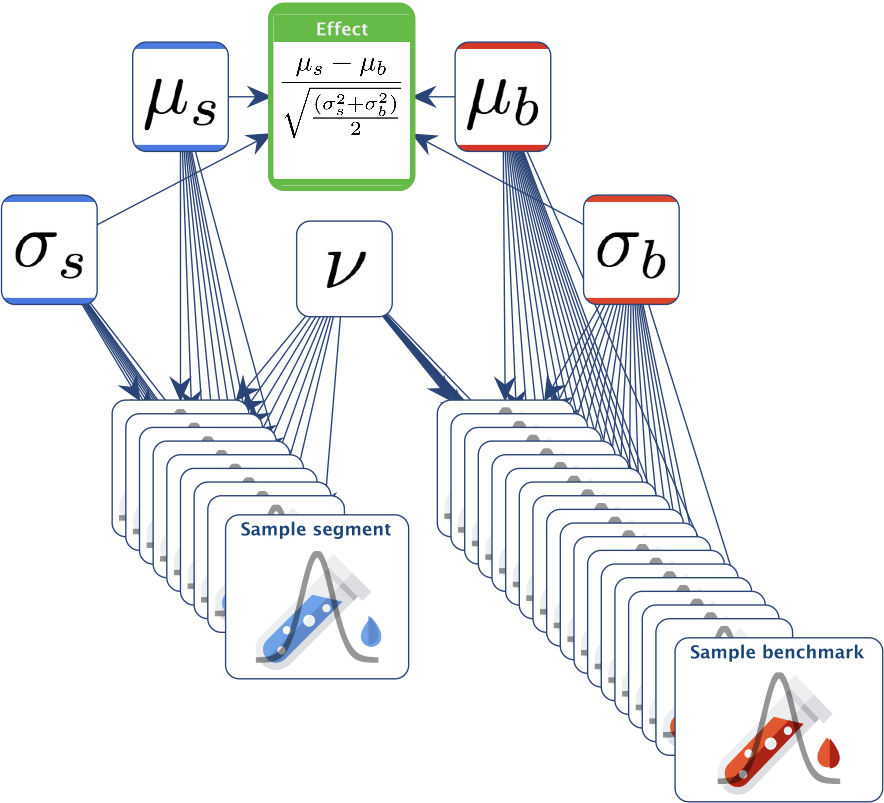
Below is the Bayesian network used in the BEST approach. We assume that the samples follow a Student’s t-distribution.
-
The segment and the benchmark have their own and , but they share the same .
- The default Confidence Level has been set to 95%. This is the same for both tests.
- As for the Bayesian test, the Region of Practical Equivalence (ROPE) on the effect size around the null value has been set by default to [-0.1, 0.1].
- The null value is rejected if the 95% Highest Density Interval (HDI) falls completely outside the ROPE.
- Under
Main Menu > Window > Preferences, you can modify:- the confidence level (for both the t-test and BEST),
- the Markov Chain Monte Carlo parameters used for inference in the Bayesian network described above,
- the ROPE size that defines an interval centered at 0, i.e., 0.2 defines the interval [-0.1, 0.1].
Example
- Checking Null Value Assessment triggers the computation of both tests.
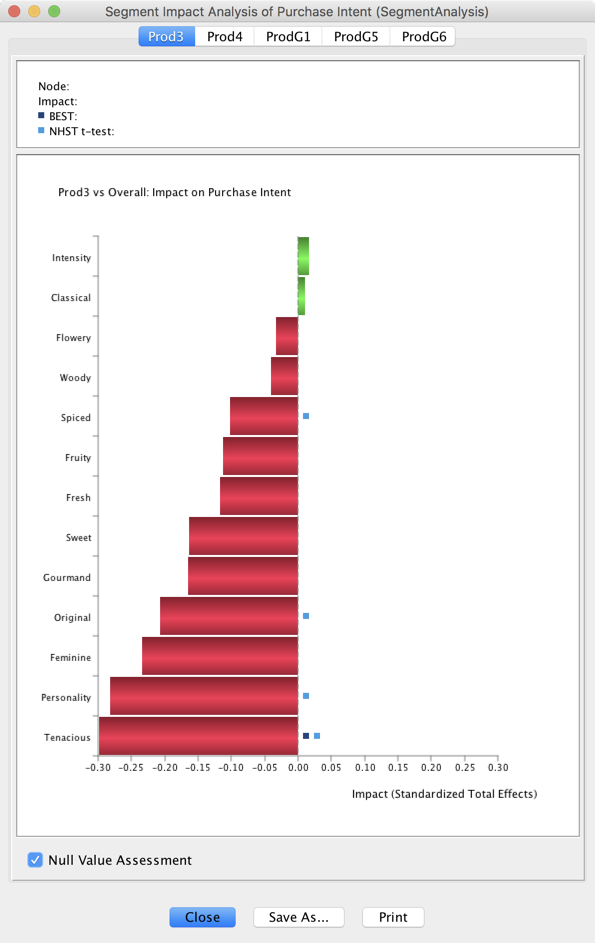
- If the mean values are estimated as significantly different, a square is added next to the Impact bar:
-
 for the t-test
for the t-test -
 for BEST
for BEST
-
