Variable Clustering
Context
- This tool clusters nodes into groups based on their “proximity,” as measured by the Arc Force.
Usage
- Select
Main Menu > Learning > Clustering > Variable Clusteringor use the shortcutS. - A color is automatically associated with each cluster to highlight the clustering:
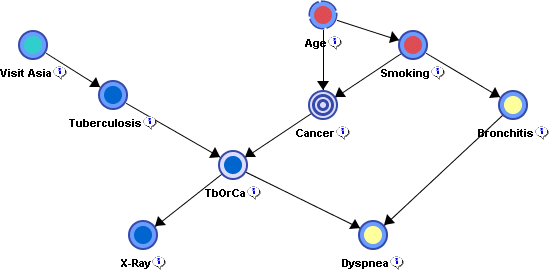
- The number of clusters is automatically computed by using the Arc Force metric.
- The associated toolbar contains a slider that allows you to choose the desired number of clusters, e.g., 4 in the previous example:

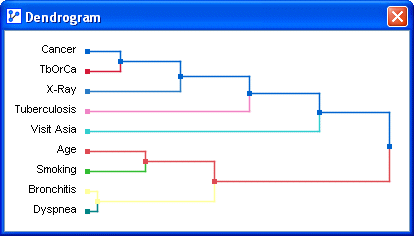
- Clicking on the Dendrogram icon displays a hierarchical representation of the current clustering as a dendrogram. You can modify the number of clusters and observe the result immediately in the dendrogram.
- A contextual menu allows displaying the comment associated with the node instead of the name.
- You can also copy the graph as an image.
- The length of the links joining the clusters is inversely proportional to the strength of the relationships between the two sets of variables: the shorter the link, the stronger the relationship.
If the cursor is moved over the junction point of the links in the Dendrogram, a tooltip displays the Arc Force.
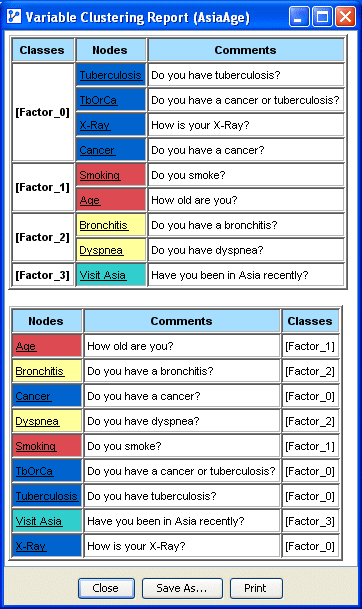
Clicking the Validate validates the current clustering and associates each set of variables with a Class named [Factor_i]. Furthermore, an HTML report of the current clustering is displayed:
Clicking the Stop icon concludes the Variable Clustering.
Once the classes are created and associated with the clusters, you can perform Multiple Clustering, which generates, for each class named [Factor_i], a synthetic variable from the nodes belonging to this class.
The number of clusters automatically determined by the algorithm can be limited by the option in the settings. The user can also modify the stop threshold corresponding to the maximum KL weight a cluster can reach.
