Discrete Probability Distributions
NoisyOr(s, leak, c1, p1, cn, pn)
-
Description: This function represents a noisy OR in which the effect of the parents (the causes
ci) on the symptomscan be inhibited.pirepresents the probability that the causeiacts on the symptom (the inhibition probability is then1 - pi). It is also possible to define aleakprobability for the set of causes that are not directly modeled. -
Number of parameters: even, and >= 4
-
Parameter type: boolean, numerical, boolean, numerical, …, boolean, numerical
-
Result type: real
Example
The conditional probability table below corresponds to NoisyOr(?N3?, 0.1, ?N1?, 0.8, ?N2?, 0.6):
| N1 | N2 | N3 = False | N3 = True |
|---|---|---|---|
| False | False | (1 - 0.1) | 0.1 |
| False | True | (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.6) | 0.64 |
| True | False | (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.8) | 0.82 |
| True | True | (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.8) * (1 - 0.6) | 0.928 |
NoisyAnd(s, leak, c1, p1, cn, pn)
-
Description: This function represents a noisy AND, i.e., the noisy OR negation.
-
Number of parameters: even, and >= 4
-
Parameter type: boolean, numerical, boolean, numerical, …, boolean, numerical
-
Result type: real
Example
The conditional probability table below corresponds to NoisyAnd(?N3?, 0.1, ?N1?, 0.8, ?N2?, 0.6):
| N1 | N2 | N3 = False | N3 = True |
|---|---|---|---|
| False | False | 0.928 | (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.6) * (1 - 0.8) |
| False | True | 0.82 | (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.8) |
| True | False | 0.64 | (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.6) |
| True | True | 0.1 | (1 - 0.1) |
Binomial(k, n, p)
-
Description: Probability of obtaining exactly
koccurrences of the same event of probabilitypamongnindependent experiments. -
Number of parameters: 3
-
Parameter type: integer, integer, numerical
-
Result type: real
Example
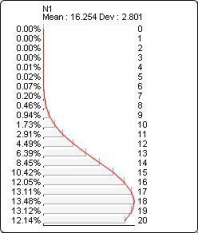
The probability distribution below corresponds to Binomial(?N1?, 20, 0.3):
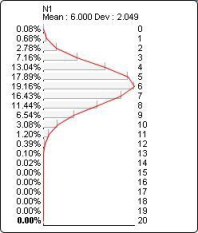
NegBinomial(k, n, p)
-
Description: Probability of requiring
ktrials to havensuccesses of the same event of probabilitypamong independent experiments. -
Number of parameters: 3
-
Parameter type: integer, integer, numerical
-
Result type: real
Example
The probability distribution below corresponds to NegBinomial(?N1?, 4, 0.3):
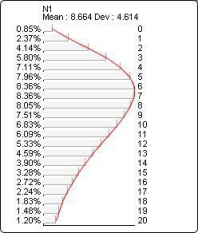
Geometric(k, p)
-
Description: Probability of requiring
kindependent experiments to obtain a first observation of an event of probabilityp. -
Number of parameters: 2
-
Parameter type: integer, numerical
-
Result type: real
Example
The probability distribution below corresponds to Geometric(?N1?, 0.3):
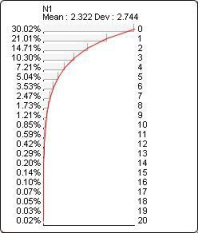
Hypergeometric(k, n, m, N)
-
Description: Probability of obtaining
kwinning objects when choosingnobjects amongN, wheremare winning objects. -
Number of parameters: 4
-
Parameter type: integer, integer, integer, integer
-
Result type: real
Example
The probability distribution below corresponds to Hypergeometric(?N1?, 5, 5, 20):
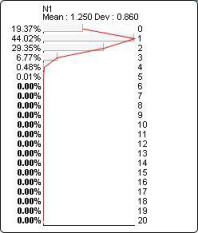
Poisson(k, l)
-
Description: Probability of obtaining
kobservations of an event in a large number of independent experiments when the mean isl. -
Number of parameters: 2
-
Parameter type: integer, real
-
Result type: real
Example
The probability distribution below corresponds to Poisson(?N1?, 18.5):
DiscUniform(k, a, b)
-
Description: Uniform distribution defined by the discrete interval [a, b].
-
Number of parameters: 3
-
Parameter type: integer, integer, integer
-
Result type: real
