Normalized Mutual Information
Definition
Based on Mutual Information, Normalized Mutual Information includes a normalization factor:
where denotes the number of states of .
This means that the Mutual Information is divided by the maximum possible entropy of , i.e., .
With that, the formal definition of Normalized Mutual Information is:
Usage
BayesiaLab reports the Normalized Mutual Information in the Target Analysis Report: Menu > Analysis > Report > Target > Relationship with Target Node.
Note that this table shows the Normalized Mutual Information of each node, e.g., XRay, Dyspnea, etc., with regard to the Target Node, Cancer.
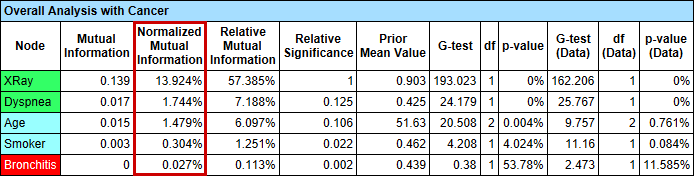
The Normalized Mutual Information can also be shown by selecting Menu > Analysis > Visual > Overall > Arc > Mutual Information and then clicking the Show Arc Comments icon or selecting Menu > View > Show Arc Comments.
Note that the corresponding options under Menu > Preferences > Analysis > Visual Analysis > Arc's Mutual Information Analysis have to be selected first:
- In Preferences, Child refers to the Normalized Mutual Information from the Parent onto the Child node, i.e., in the direction of the arc.
- Conversely, Parent refers to the Normalized Mutual Information from the Child onto the Parent node, i.e., in the opposite direction of the arc.
