Direct Structural Network Comparison
Context
- Structural Network Comparison is a tool in BayesiaLab to compare networks in terms of their structure.
- On this page, we explain how to launch Structural Network Comparison directly from the Main Menu.
- Because you can directly access this tool from the Main Menu and directly select which networks to compare, we refer to it here as Direct Structural Network Comparison.
- A limitation of the Direct Structural Network Comparison is that it can only compare two networks, i.e., your current network as the Reference Network and one Comparison Network.
- Alternatively, you can start Structural Network Comparison from within certain analysis functions, i.e., “in an analysis context”, which is explained here: Structural Network Comparison in Analysis Context.
Usage
The Direct Structural Network Comparison is accessible from the Main Menu, both in the Modeling and the Validation Mode:
-
Select
Main Menu > Tools > Compare > Structure. -
A window opens up with the current network displayed in the left panel as the so-called Reference Network.
-
The right panel is initially blank, but by clicking on the No Comparison Network button, you can select any saved Bayesian network file (in XBL format) that consists of the same nodes as the Reference Network. Typically, you would compare networks that you generated by applying different learning algorithms to the same dataset.
-
By clicking the Reference Network button, which is labeled with the name of your current network, you can also choose an altogether different network for comparison purposes.
-
If you attempt to select incompatible networks, an error message prevents you from proceeding.
Structure Comparison Report
-
Once you click the Compare button on the basis of compatible networks, a new window opens up with the Structure Comparison Report:
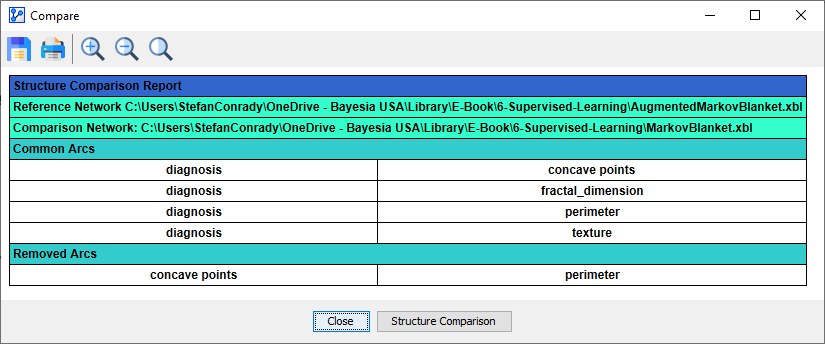
-
The report lists all differences between the Reference Network and the Comparison Network.
- Overall, there can be up to ten categories in the report:
- Common Arcs: arcs that exist in both networks.
- Inverted Arcs: arcs which orientation changes in the Comparison Network.
- Added Arcs: arcs that exist only in the Comparison Network.
- Removed Arcs: arcs that exist only in the Reference Network.
- Common Edges: edges that exist in both networks.
- Added Edges: edges that exist only in the Comparison Network.
- Removed Edges: edges that exist only in the Reference Network.
- Common V-Structures: V-structures that exist in both networks.
- Added V-Structures: V-structures that exist only in the Comparison Network.
- Removed V-Structures: V-structures that exist only in the Reference Network.
- In the sections referring to arcs, the left column represents the parent nodes associated with the arcs, i.e., the arcs’ origins. The right column lists the child nodes associated with the arcs, i.e., the arcs’ destinations.
- In the portion of the table dealing with V-structures, the outer columns list the parent nodes, while the center column shows the common child nodes.
- Overall, there can be up to ten categories in the report:
-
Clicking the Structure Comparison button opens a further window that visualizes the differences listed in the above report.
Structure Comparison Window
The Structure Comparison Window features a toolbar at the top. Some of the icons are common throughout BayesiaLab and others are specific to this particular context:
Save the currently displayed graph as an image file | |
Print the currently displayed graph | |
Show the Synthesis Structure | |
Show the Reference Structure | |
Go to the previous structure | |
| Go to the next structure | |
| Zoom In | |
| Zoom Out | |
Return to the Default Zoom Level | |
Resize the graph to fit the window | |
Position the graph at the top-left corner of the window | |
Stretch the graph or the selected nodes | |
Shrink the graph or the selected nodes | |
| Rotate Left | |
| Rotate Right | |
Save the currently displayed network as an XBL file | |
Open the currently displayed network in a new Graph Window |
Synthesis Structure
-
Upon opening the Structure Comparison Window, the Synthesis Structure appears as the default view.
-
The Synthesis Structure is marked by the icon in the toolbar and also labeled as such at the bottom of the Structure Comparison Window.
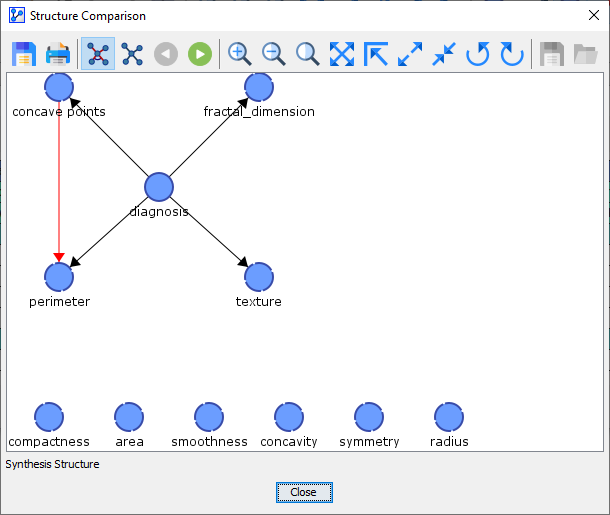
-
Although the Synthesis Structure may look like a Bayesian network, it is actually not a Bayesian network.
-
Rather, the Synthesis Structure visualizes the commonalities and differences between the Reference Network and the Comparison Network.
- A black edge or arc signifies that it exists both in the Reference Network and the Comparison Network.
- A blue edge or arc indicates that it does not exist in the Reference Network but that it does exist in the Comparison Network.
- A red edge or arc means that it does exist in the Reference Network but that it does not exist in the Comparison Network.
-
Directed arcs are displayed in the form of an arrow.
-
A directed arc is displayed as such in the Synthesis Structure if the link in question is a directed arc in both the Reference Structure and the Comparison Structure.
-
Undirected edges are shown as a straight solid line.
-
An undirected edge is displayed as such in the Synthesis Structure if the link in question is an undirected edge in either the Reference Structure or the Comparison Structure.
-
A circled line between two arcs highlights a V-structure.
Reference Structure
-
By clicking on the next button , you proceed from the Synthesis Structure to the Reference Structure.
-
Alternatively, you can access the Reference Structure by clicking on the corresponding icon.
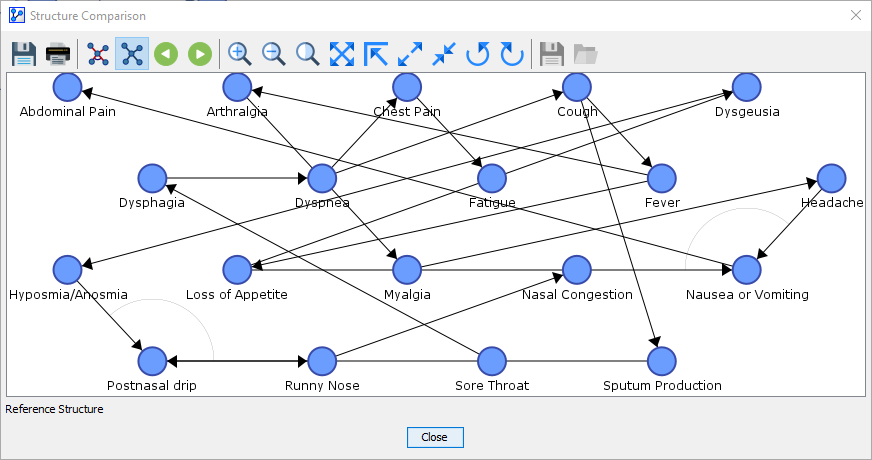
-
The Reference Structure represents the original network. Thus, what is displayed is a proper Bayesian network, not merely an illustration.
-
The only visual additions are the circled lines that highlight the V-structures in the network.
Comparison Structure
-
By clicking on the next button , you proceed from the Reference Structure to the Comparison Structure.
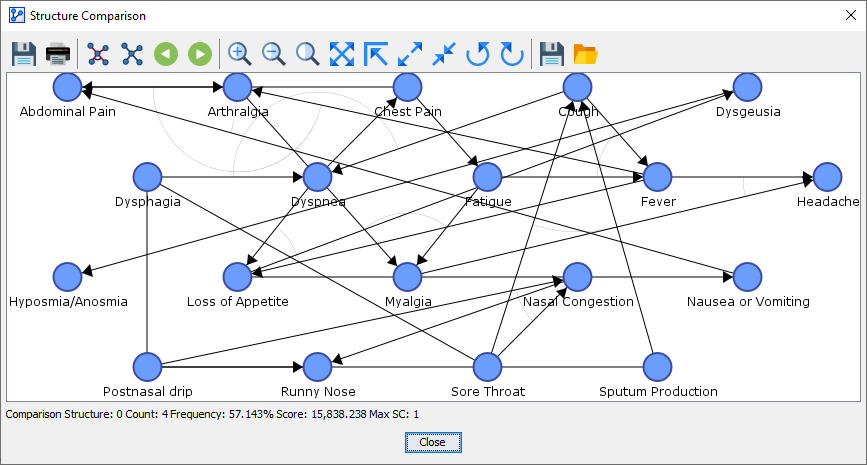
-
It is labeled as “Comparison Structure: 0” at the bottom of the window.
-
Numbering the Comparison Structure and showing its count and frequency may seem superfluous here. However, when we proceed to Structural Network Comparison in Analysis Context, there could be a range of networks to compare.
-
For the Comparison Structure, the Save Network and Open Network icons are now available. This allows you to extract the network you currently see. In the context of comparing just two networks, this may be less important. However, when comparing numerous structures that have not yet been saved, as in Structural Network Comparison in Analysis Context, it will become much more important.
