Edit Constants
Context
- Constants are useful for managing values that are used in equations throughout the network.
- For instance, Constants may represent a list of key assumptions pertaining to a problem domain.
- By storing Constants centrally, you can easily modify values and apply them universally wherever those values are used in Formulas in the network.
- In BayesiaLab, you can maintain values as Constants so they can be used in Formulas that generate probability distributions of nodes.
Usage
-
You can access the Constants Editor in three ways:
- Select
Main Menu > Edit > Edit Constants. - Select
Graph Panel Context Menu > Constants. - Click the Constants indicator in the Status Bar.
- Select
-
A new window opens featuring the Constants Editor:
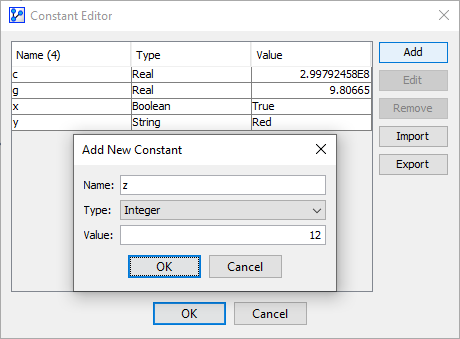
-
In the Constants Editor, you can perform a range of operations:
-
Add: Create a new Constant.
-
Edit: Modify an existing Constant.
-
Remove: Remove an existing Constant.
-
Import: Import a text file that contains Constant definitions in the format
<Constant>=<Type><Space><Value>, as in the following example:c=REAL 2.99792458E8 g=REAL 9.80665 x=BOOLEAN true y=STRING Red z=INTEGER 12 -
Export: Export a text file with the current Constant definitions.
-
General Requirements for Constants
- A Constant must have a unique name.
- A Constant can be of types Boolean, Integer, Real, or String.
- In Formulas, Constants are referenced by name.
- Constants exist in the “background” and are not shown as nodes in the network.
- As a result, Constants do not need to be connected to the nodes that utilize them. Rather, Constants can be accessed in any Formula throughout the network merely by referencing their names.
- Constants can be created and modified only in Modeling Mode.
- When switching from Modeling Mode into Validation Mode, the conditional probability tables of nodes that are defined by equations and Constants are recomputed according to the current values of those Constants.
- Once you have created a Constant, you can subsequently modify it at your discretion.
Example & Workflow Illustration
- The following example illustrates a Bayesian network that models profitability as a function of inventory and demand.
- For our purposes, we focus on the random node Demand.
- We will define its probability table for Demand using a Probabilistic Formula Equation and Constants.
- More specifically, we define the distribution of Demand as a Normal distribution with the mean Demand Forecast and the standard deviation Demand Forecast Uncertainty:
- The workflow contains the following steps:
- Select
Graph Panel Context Menu > Edit Constants. - In the Constants Editor, click Add.
- Set Name, Type, and Value of the new Constant.
- Click OK to close the Constants Editor.
- Double-click the node Demand, which opens the Node Editor.
- Open the
Probability Distribution > Formulatab. - Set Return Type to Probabilistic.
- From the Continuous Probability Distributions folder, double-click on Normal(x, m, s) to add it as a function template to the Formula Editor.
- Double-click on Demand in the center panel to replace the x placeholder.
- Double-click on Constants to show the available Constants in the right panel.
- Double-click Demand Forecast and Demand Forecast Uncertainty to place them into the m and s placeholders, respectively.
- Click Validate.
- Click OK to close the Formula Editor.
- Switch to Validation Mode.
- Double-click the node Demand to bring up the corresponding Monitor in the Monitor Panel.
- Review the distribution shown on the Monitor of Demand.
- Select
