Node Editor — Properties
Context
- The Properties tab in the Node Editor allows you to define and modify a range of characteristics of a node.
Usage
-
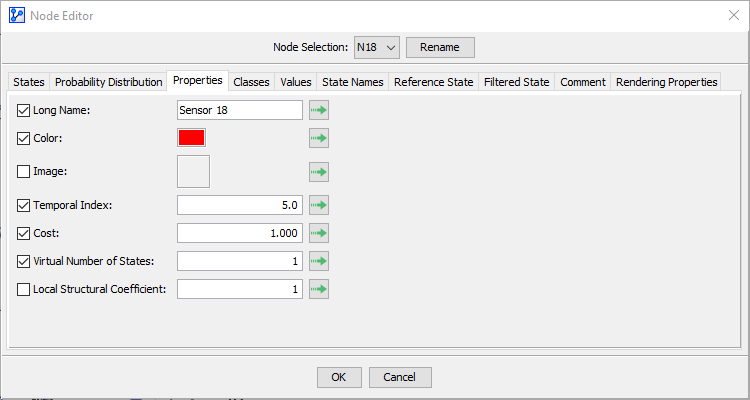
In the Node Editor, select the Properties tab.
-
Within this tab, you can select and deselect, as well as edit node properties.
-
See the following topics for a detailed description of each property.
This panel allows editing several node properties. Each property is also available from the node’s context menu.
- Color: Allows displaying a colored tag on the node, its comment, and its monitor. Checking the option or clicking the preview rectangle opens the color chooser dialog. Once a color is selected, it is displayed inside the rectangle and can be modified by clicking the rectangle again. To remove the color, uncheck the option. The Propagate Color to the Classes button displays a dialog to select the classes associated with the node for propagation. In this case, all nodes in those classes display the same selected color, or the default if no color is selected.
- Image: Allows displaying an image instead of the node’s default representation. Checking the option or clicking the preview rectangle opens the file chooser dialog to select an image. The display size is 30 x 30. If an image is larger, it is reduced; if it is smaller, it is centered. The image is saved in the network file. To remove the image, uncheck the option. The Propagate Image to the Classes button displays a dialog to select the classes associated with the node for propagation. In this case, all nodes in those classes display the same selected image, or none if no image is selected.
- Temporal Index: Allows associating a temporal index with the node. This index is a positive or zero integer and indicates a temporal order between nodes that is taken into account by the learning algorithms. A node with a temporal index greater than the temporal index of another node cannot be its ancestor. To remove the index, uncheck the option. The Propagate Index to the Classes button displays a dialog to select the classes associated with the node for propagation. In this case, all nodes in those classes will have the same index, or none if there is no index.
- Cost: Allows associating a cost with the node. The cost is a real number greater than or equal to 1 and represents the cost of an observation. The cost is used in the Adaptive Questionnaire. It is possible to make a node Not Observable by unchecking the option. In this case, the node will not be proposed in the Adaptive Questionnaire. It is also possible to use the Not Observable cost to ignore values read from a database (Interactive Inference, Batch Labeling, Batch Joint Probability), to indicate the node to update (Interactive Bayesian Updating), or to indicate the node for which you want to compute the posterior probability distribution for each case described in a database (Batch Inference). The Propagate Cost to the Classes button displays a dialog to select the classes associated with the node for propagation. In this case, all nodes in those classes will have the same cost, or will be not observable if there is no cost.
- State Virtual Number: Allows replacing the real number of states during learning with a virtual number for the MDL score. The node’s state count has an important impact on the MDL score computed during structural learning, so this setting lets you influence structural complexity locally. The more states a node has, the less chance it has of having linked parents during learning, and vice versa. Decreasing this parameter decreases the MDL score of the node, and vice versa. The Propagate State Virtual Number button displays a dialog to select the classes associated with the node for propagation. In this case, all nodes in those classes will have the same state virtual number, or none if there is no value.
- Local Structural Coefficient: This parameter acts like the network’s Global Structural Coefficient but applies to each node. It can increase or decrease the structural complexity of the network at the node level. This parameter acts on the whole MDL score of the node, unlike the state virtual number. The higher a node’s MDL score, the less chance it has of having linked parents during learning, and vice versa. Decreasing this parameter decreases the node’s MDL score, and vice versa. The Propagate Local Structural Coefficient button displays a dialog to select the classes associated with the node for propagation. In this case, all nodes in those classes will have the same local structural coefficient, or none if there is no value.
- Exclusion: A node can be excluded during structural learning, meaning the learning algorithm will not add any arc having this node as an extremity. This is particularly useful if you wish to learn the structure of a network on a subset of nodes. The Propagate Exclusion button displays a dialog to select the classes associated with the node for propagation. In this case, all nodes belonging to these chosen classes will be excluded or not.
