Information Gain (9.0)
Context
The Log-Loss LL(E) reflects the cost to process a particle E with a model, i.e. the number of bits that are needed to encode the particle E given the model. The lower the probability is, i.e. the more surprising a particle is given our model, the higher the log-loss is.
where P(E) is the joint probability of the n-dimensional evidence E returned by the Bayesian network:
The Information Gain is the difference between the cost to process a particle E with the fully unconnected network (the straw model S, where all nodes are marginally independent), and the cost with the current Bayesian network B:
Usage
Select Menu > Analysis > Report > Evidence > Information Gain
History
This function, previously called Evidence Analysis Report, has been first updated in version 5.0.2.
Renamed Metrics: Local Information Gain
The metric used to compare the cost to represent the posterior probability of the 1-piece of hypothetical evidence h given the current set of evidence E and its prior probability is now called Local Information Gain instead of Information Gain.
Renamed Metrics: Hypothetical Information Gain
What would be the Information Gain if h, a 1-piece of evidence, were added to the current set of evidence E? This metric was called Bayes Factor in the previous releases.
New Feature: Analysis of the Selected Nodes Only
As of version 9.0, the analysis can be carried out on the selected nodes only.
Example
Let’s use the network below with the following three pieces of evidence E:
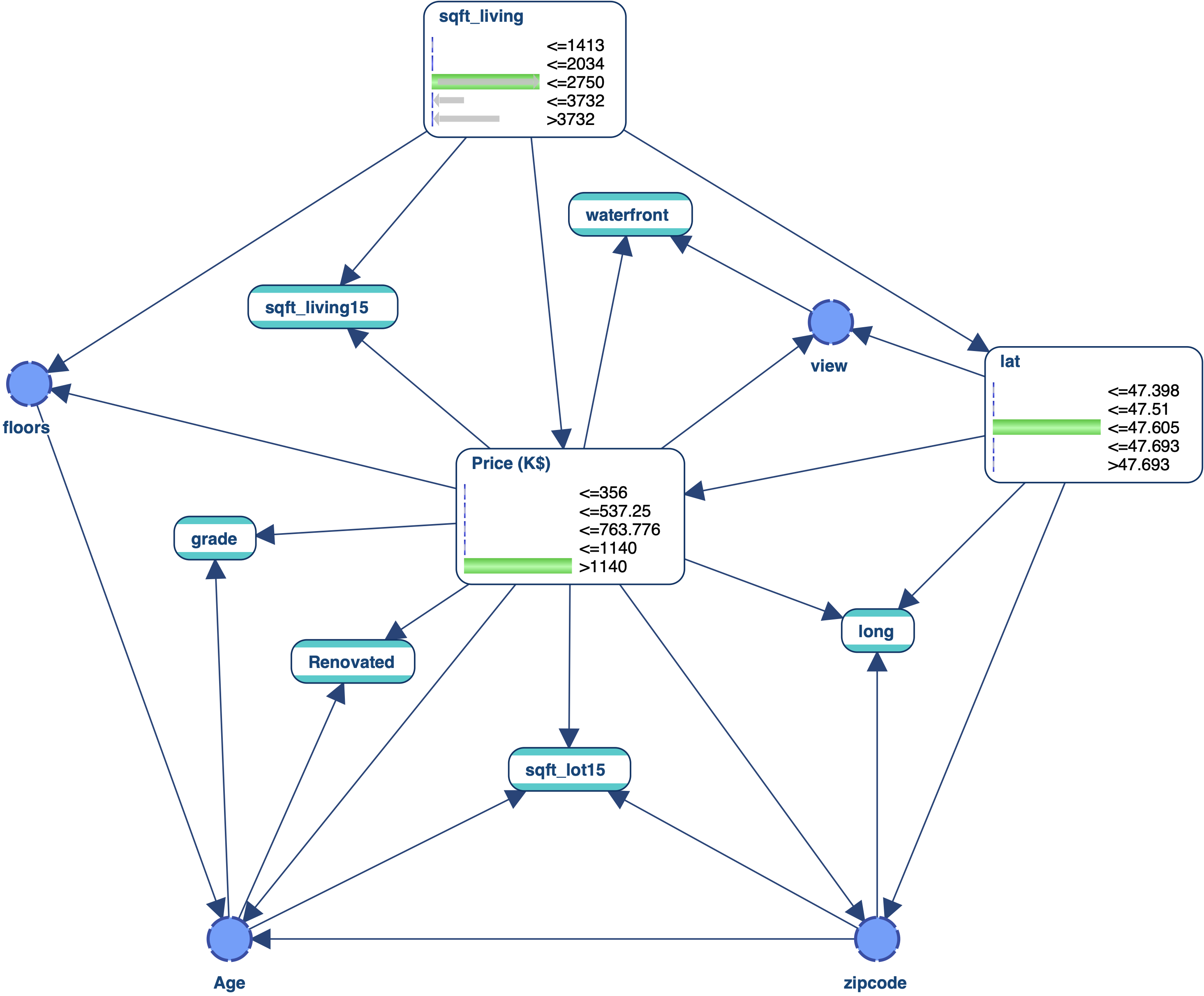
We select the nodes , , , , and and run the analysis on these five nodes only:
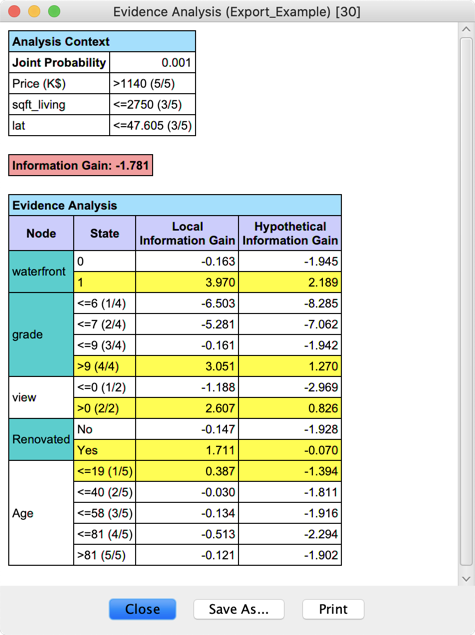
As we can see, the Information Gain of E with this network is negative (-1.781). A negative Information Gain is sometimes referrsed to a “conflict.”
However, if we were to add the evidence , this would make the Information Gain of the new set of evidence positive (2.189). As such, this est of evidence is considered “consistent.”
