Cluster Interpretation: Relationship with Target Node
Background & Context
- On this page, we present the Relationship with Target Node report for cluster interpretation as an alternative to Most Relevant Explanations for Cluster Interpretation.
- To provide further context for Most Relevant Explanations for Cluster Interpretation, we compare several other approaches that can help interpret individual Clusters:
- Setting Evidence for Cluster Interpretation: Posterior Distributions, Relationship with Target Node, Mosaic Analysis, Posterior Mean Analysis, Segment Profile Analysis, Histograms, Tornado Diagrams,
- Optimization for Cluster Interpretation: Dynamic Profile, Target Optimization Tree
- More specifically, we compare all these approaches with regard to characterizing the state Cluster 3 of the Cluster Node Factor\_0\ in the reference network.
- All analyses and instructions on this page refer to this reference network, which you can download here:
MaleClusters.xbl
Relationship with Target Node
- To produce the Relationship with Target Node report, select Main Menu > Analysis > Report > Target > Relationship with Target Node.
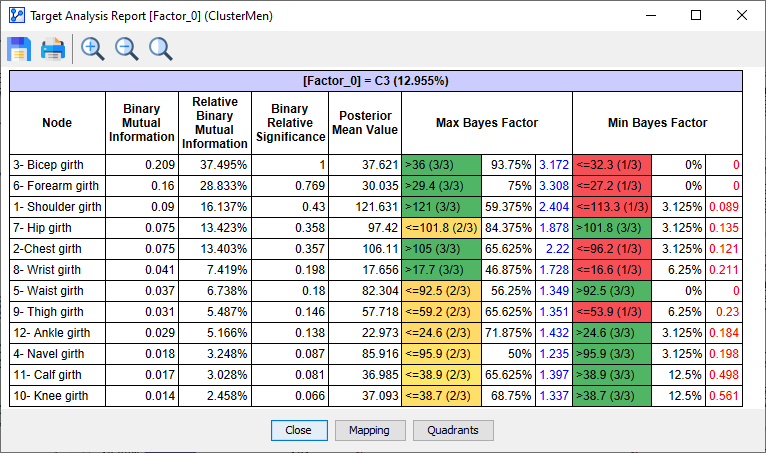
- In addition to a wide range of information about the Target Node in general and the other states, we obtain a list of measures specific to Cluster C3:
- Node: name of the node to which all measures of the row apply.
- Binary Mutual Information: the amount of information gained by observing the node regarding the Target State (C3) of the Target Node Factor\_0\.
- Note that in an earlier table within this report, BayesiaLab reports the Mutual Information of the node regarding the Target Node in general.
- Relative Binary Mutual Information: the amount of information gained by observing the node regarding the Target State (C3) of the Target Node Factor\_0\, divided by the marginal Entropy of the Target State.
- Binary Relative Significance: the proportion of the node's Binary Mutual Information relative to the node with the maximum Binary Mutual Information. As a result, the top row always features a Binary Relative Significance of 1.
- Posterior Mean Value: the expected value of the node given Target State (C3) of the Target Node Factor\_0\.
- The Max Bayes Factor heading spans three unlabeled columns:
- Node State that corresponds to the maximum Bayes Factor for that node regarding Target State (C3) of the Target Node Factor\_0\. In addition to the State Value (or State Name)
- Probability of the Node State with the Maximum Bayes Factor.
- Bayes Factor calculated for that state.
- The Min Bayes Factor heading spans three unlabeled columns:
- Node State that corresponds to the minimum Bayes Factor for that node regarding Target State (C3) of the Target Node Factor\_0\. In addition to the State Value (or State Name)
- Probability of the Node State with the Minimum Bayes Factor.
- Bayes Factor of the Node State with the Minimum Bayes Factor.
